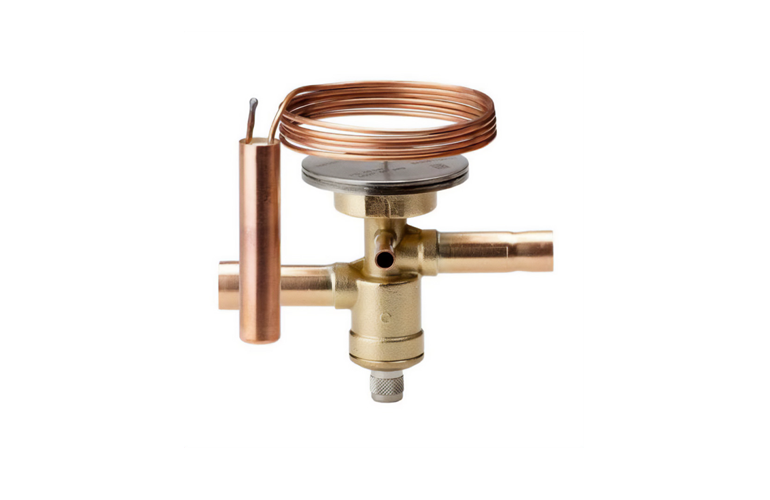
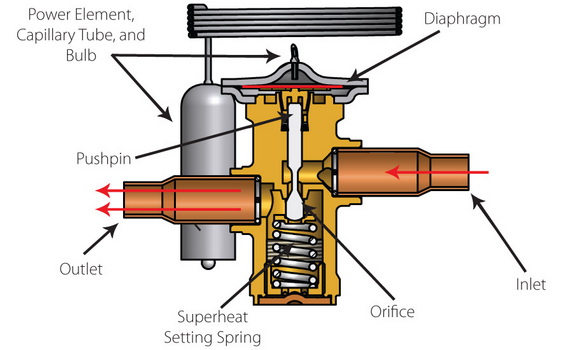
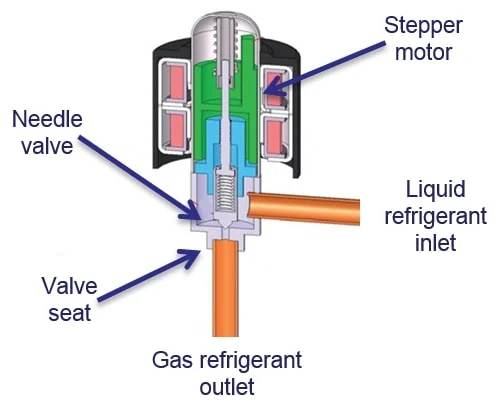
1. Precision and Flexibility : The EXV can control refrigerant flow with exceptional accuracy, improving system performance under all conditions.
2. Dynamic Control : It can instantly adapt to changes in temperature, pressure, and other parameters, ensuring enhanced energy efficiency.
3. Energy Efficiency : Precise and continuous flow adjustment leads to significant energy savings, which is especially important for large installations or systems with variable demand.
4. Reduced Wear : Due to its accurate and controlled operation, wear on other system components (such as the compressor) is minimized, resulting in a longer service life.